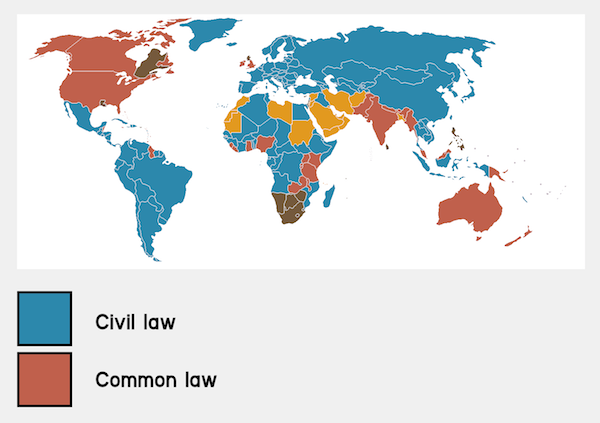
- The key differences between common law and civil law systems lie in their approaches to legal precedents, the codification of laws, judicial decision-making, and the handling of contracts.
- Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in legal disputes or those interested in the legal landscape of different countries.
Understanding Precedent in Common Law
One fundamental distinction in common law systems lies in the role of legal precedents. These precedents are established through past court decisions and play a crucial role in future rulings. Lawyers often reference earlier cases to influence court decisions, although the impact of legal scholars is typically limited. This system of precedent ensures that similar cases receive similar treatment unless significant differences justify an alternate ruling.
Codification and Flexibility in Civil Law
In contrast, civil law is characterized by codified statutes that are created through legislative processes. This system provides less room for interpretation since laws are explicitly written and updated by governmental bodies. Civil law governs non-criminal disputes such as personal rights and property issues, focusing more on applying laws to specific cases than on setting precedents.
Crime and Punishment: The Common Law Approach
Common law directly addresses criminal activities, defining and dealing with crimes like theft, assault, or murder. The outcome of such cases depends heavily on the evidence presented and past judicial decisions, which are binding. This system emphasizes the presumption of innocence and bases judgments on the ability to prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt.
Civil Law and Non-Criminal Disputes
Meanwhile, civil law deals with legal disputes that do not involve criminal charges, such as negligence or other claims of injury. Decisions in these cases impact only the parties involved and are not generally used to set precedents affecting future cases, although they may influence legislative changes or lead to new laws.
Judicial Decision-Making in Diverse Legal Systems
Judicial decisions vary significantly between common and civil law systems. In common law countries, judges make rulings based on past decisions and the strict application of existing laws. Civil law judges, however, have more flexibility to interpret the law based on the specifics of each case, which may lead to legal reforms or adjustments in how laws are applied.
The Role of Contracts in Legal Disputes
Contracts play a pivotal role in both legal systems but are treated differently. Common law typically deals with explicitly stated terms within contracts, with fewer implied terms. Civil law, however, includes a broader interpretation of implied terms, which can lead to disputes being settled more frequently in civil courts, especially in cases involving complex agreements like offshore banking.
The Importance of Qualified Legal Representation
Regardless of the legal system, the importance of competent legal representation cannot be overstressed. An experienced attorney can navigate the complexities of either system to help clients understand their legal standing and the best course of action based on the specifics of their case.