The Arctic, often perceived as a remote and icy expanse, is increasingly becoming a hotbed of geopolitical intrigue and economic interest. The gradual warming of the climate and the resultant melting of polar ice have made this region more accessible than ever, unveiling vast untapped resources and sparking a complex interplay of power among global heavyweights.
Hidden Treasures Beneath the Ice
The Arctic is estimated to hold about 90 billion barrels of oil and 1.67 trillion cubic meters of natural gas, constituting up to 22% of the world’s unexploited oil and gas reserves. This revelation, sourced from the US Geological Survey, has turned the Arctic into a potential goldmine for energy resources.
The Financial Forecast
Predictions suggest that the Arctic could generate at least $100 billion annually from investments in the extraction industry in the coming years. This economic potential is drawing significant attention from countries and corporations alike, eager to tap into these lucrative opportunities.
A Domain Without Sovereignty
The absence of an international agreement regulating the North Pole territories creates a competitive environment. Countries bordering the Arctic, each with their vested interests, are vying for influence and control over these valuable resources.
Russia’s Arctic Aspirations
Russia, possessing about 50% of the Arctic coastline and the world’s largest fleet of icebreakers, including nuclear-powered units, is a major player in the region. With ambitious plans like establishing 15 cities on the Taymyr Peninsula, Russia’s investment in Arctic infrastructure, including ports and airports, is substantial. Partnerships between Gazprom, Rosneft, and other entities could see investments reaching up to $500 billion.

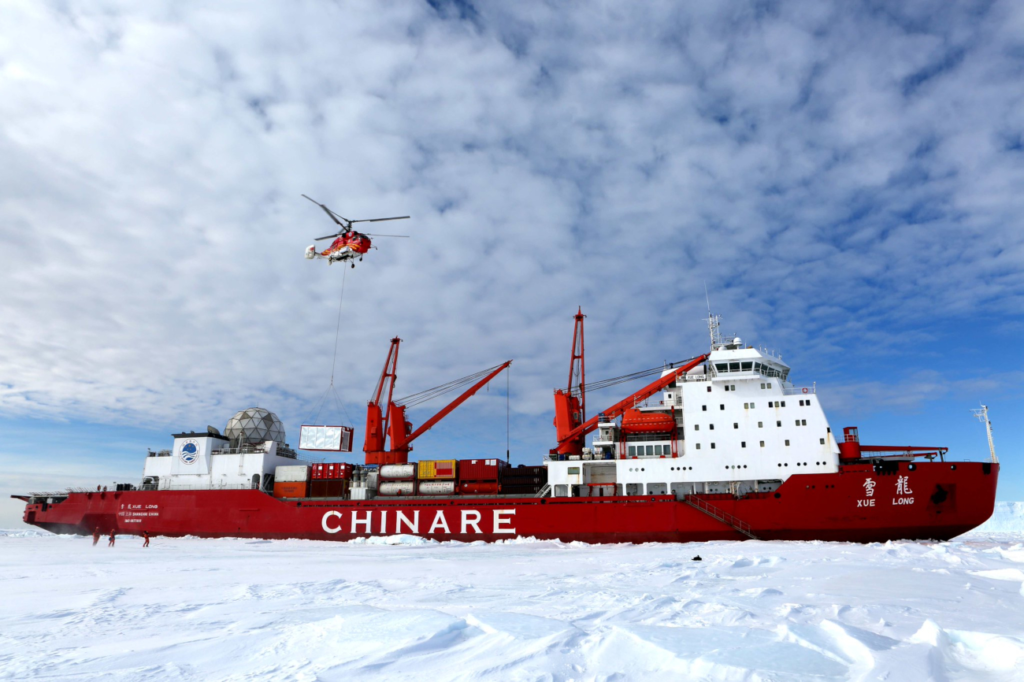
China’s Polar Strategy
China, in collaboration with Russia, is working towards becoming a “polar power” by 2030. Its investments in Arctic oil fields, totaling approximately $80 billion, reflect its strategic interest in the region’s resources.
The United States’ Approach
The US, through Alaska, is directly impacted by Arctic developments. The Biden administration’s stance on sustainable development and international cooperation, including the prohibition of oil extraction in certain areas, contrasts with the more aggressive resource exploitation strategies of other nations. Despite a significant military presence in Alaska, the US faces challenges in matching Russia’s military and infrastructural advantages in the Arctic.

Canada’s Environmental Focus
Canada, another key player with a significant Arctic border, has also halted further investments in resource extraction, aligning with a more environmentally conscious approach.
Despite the increasingly favorable climate for extraction activities, the Arctic remains a hostile environment. Huge waves and extreme temperatures necessitate substantial investments in infrastructure and safety measures, underscoring the complexity and risks associated with Arctic resource exploitation.










